Teollisista lähteistä löytyy hyvä luettelo suoraketjuisista dikarboksyyihapoist. ihmiskehossa tärkeät olen merkinnyt tummalla. Näillä on omat spesifiset aineenvaihduntansa , mm. ne littyvät proteiineihin transsylaatiossa ja niitä siirretään deasylaatioissa( tästä erikseen 20.7. 2018).
http://chemicalland21.com/industrialchem/organic/SUCCINIC%20ACID.htm
There are almost infinite esters obtained from carboxylic acids. Esters are formed by removal of water from an acid and an alcohol. Carboxylic acid esters are used as in a variety of direct and indirect applications. Lower chain esters are used as flavouring base materials, plasticizers, solvent carriers and coupling agents. Higher chain compounds are used as components in metalworking fluids, surfactants, lubricants, detergents, oiling agents, emulsifiers, wetting agents textile treatments and emollients, They are also used as intermediates for the manufacture of a variety of target compounds. The almost infinite esters provide a wide range of viscosity, specific gravity, vapor pressure, boiling point, and other physical and chemical properties for the proper application selections.
C
length (Straight)
|
Product
|
CAS
#
|
Melting
Point
|
Boiling Point |
| C 2 | Oxalic
Acid (Ethanedioic Acid) |
144-62-7 | 189 - 191 C | Sublimes |
| C 3 | Malonic
Acid (Propanedioic Acid) |
141-82-2 | 131 - 135 C | Decomposes |
| C 4 | Succinic
Acid (Butanedioic Acid) |
110-15-6 | 185 - 190 C | 235 C |
| C 5 | Glutaric
Acid (Pentanedioic Acid) |
110-94-1 | 95 - 99 C | 302 C |
| C 6 | Adipic
Acid (Hexanedioic Acid) |
124-04-9 | 151 - 153 C | 265 C at 100 mmHg |
| C 7 | Pimelic
Acid (Heptanedioic Acid) |
111-16-0 | 105 - 106 C | 212 C at 10 mmHg |
| C 8 | Suberic
Acid (Octanedioic Acid) |
505-48-6 | 143 - 144 C | 230 C at 15 mmHg |
| C 9 | Azelaic
Acid (Nonanedioic Acid) |
123-99-9 | 100 - 103 C | 237 C at 15 mmHg |
| C 10 | Sebacic
Acid (Decanedioic Acid) |
111-20-6 | 131 - 134 C | 294 at 100 mmHg |
| C 11 | Undecanedioic acid | 1852-04-6 | 109 - 110 C | |
| C 12 | Dodecanedioic acid | 693-23-2 | 128 - 129 C | 245 C at 10 mmHg |
| C 13 | Brassylic acid (Tridecanedioic acid) |
505-52-2 | 112 - 114 C | |
| C 14 | Tetradecanedioic acid | 821-38-5 | 126 - 128 C | |
| C 15 | Pentadecanedioic acid | 1460-18-0 | ||
| C 16 | Thapsic acid (Hexadecanedioic acid) |
505-54-4 | 124 - 126 C | |
| C 18 | Octadecanedioic acid | 871-70-5 |
- Boy Cornils & Peter Lappe:Dicarboxylic Acids, Aliphatic, Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2010. Viitattu 09.05.2013
- Löytyy myös suomalainen wikipediataulukko dikarboksyylihapoista, josa niiden nimi ja struktuuri näkyy. https://fi.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dikarboksyylihapo
Dikarboksyylihapot ovat orgaanisia yhdisteitä, joissa funktionaalisena ryhmänä
on kaksi karboksyyliryhmää -COOH. Molekyylikaavoissa dikarboksyylihapot
voidaan ilmaista yleisessä muodossa ”HOOC-R-COOH”, jossa R kuvaa
tavallisesti jotain hiilivetyketjua.
Esimerkkejä dikarboksyylihapoista
| Triviaalinimi | IUPAC nimi | Kemiallinen kaava | Rakenne |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oksaalihappo | etaanidihappo | HOOC-COOH | |
| Malonihappo | propaanidihappo | HOOC-(CH2)-COOH | |
| Meripihkahappo Sukkiinihappo |
butaanidihappo | HOOC-(CH2)2-COOH | |
| Glutaarihappo | pentaanidihappo | HOOC-(CH2)3-COOH | |
| Adipiinihappo | heksaanidihappo | HOOC-(CH2)4-COOH | 
|
| Pimeliinihappo | heptaanidihappo | HOOC-(CH2)5-COOH | |
| Suberiinihappo Korkkihappo |
oktaanidihappo | HOOC-(CH2)6-COOH | 
|
| Atselaiinihappo | nonaanidihappo | HOOC-(CH2)7-COOH | |
| Sebasiinihappo | dekaanidihappo | HOOC-(CH2)8-COOH | 
|
| dodekaanidihappo | HOOC-(CH2)10-COOH | ||
| Fumaarihappo | (E)-buteenidihappo trans-1,2-etyleenidikarboksyylihappo |
HOOC-(CH)2-COOH | 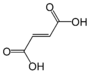
|
| Maleiinihappo | (Z)-buteenidihappo cis-1,2-etyleenidikarboksyylihappo |
HOOC-(CH)2-COOH | 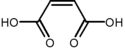
|
| Ftaalihappo | 1,2-bentseenidikarboksyylihappo orto-ftaalihappo |
C6H4(COOH)2 | 
|
| Isoftaalihappo | 1,3-bentseenidikarboksyylihappo meta-ftaalihappo |
C6H4(COOH)2 | 
|
| Tereftaalihappo | 1,4-bentseenidikarboksyylihappo para-ftaalihappo |
C6H4(COOH)2 |  |
Inga kommentarer:
Skicka en kommentar